

Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-11-26 Origin: Site











Insulin pens have become one of the most popular and convenient tools for managing diabetes. They offer a simple, portable, and discreet way for people with diabetes to administer insulin, making daily injections much easier compared to traditional syringes. Insulin pens are designed to provide precise doses, allowing users to manage their blood sugar levels effectively. However, while insulin pens are designed for ease of use, incorrect usage can lead to significant errors that affect insulin delivery and blood sugar control. These mistakes can cause fluctuations in blood sugar levels, potentially leading to serious health complications. In this article, we will discuss the most common mistakes people make when using insulin pens and offer practical tips on how to avoid them to ensure you’re getting the most accurate and effective insulin delivery for your diabetes management.
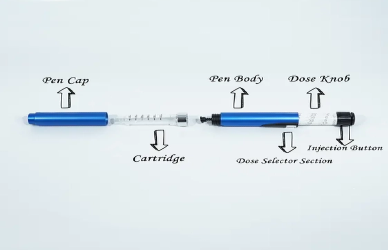
Priming the insulin pen is the process of preparing the pen for use by removing air bubbles from the cartridge before injecting insulin. It involves dialing a small dose and pressing the button to expel a tiny amount of insulin through the needle. This ensures that air is cleared from the insulin chamber and that the pen will deliver an accurate dose of insulin during injection. Priming is especially important when using a new pen or after a pen has been unused for a period of time.
If the pen is not primed properly, air bubbles may remain inside the pen, causing inaccurate dosing. When you attempt to inject insulin, the presence of air could mean that no insulin is delivered at all, or the dose delivered may be much lower than what was dialed. This can result in high blood sugar levels, as your body will not receive the full insulin dose it needs. Additionally, injecting air can be uncomfortable, and repeated missed doses may complicate diabetes management.
Attach a New Needle: If you're using a new needle, ensure it's securely attached to the pen. Remove the protective cap from both the pen and needle.
Dial a Small Dose: Turn the dose dial to 2–3 units (or follow the manufacturer's recommendation for priming). This ensures that enough insulin is expelled to clear any air from the pen.
Hold the Pen Upright: Point the needle upwards, making sure the insulin cartridge is facing up. This helps air bubbles rise to the top of the cartridge.
Press the Button: Press the injection button to release a small amount of insulin through the needle. You should see a drop of insulin at the tip of the needle, confirming that the pen is primed and free of air bubbles.
Repeat if Necessary: If no insulin is released, repeat the priming process until you see insulin at the needle tip. This confirms that the pen is ready for use.
By following these simple steps to prime your insulin pen before each use, you can ensure accurate insulin delivery and maintain better control over your blood sugar levels.
The needle should typically be inserted at a 90-degree angle to the skin for most individuals, ensuring the insulin reaches the subcutaneous tissue. For people with less subcutaneous fat, a 45-degree angle may be better to avoid discomfort and ensure proper insulin delivery.
Incorrect insertion can lead to:
Pain: Improper angles can cause more discomfort during the injection.
Incomplete Insulin Delivery: If the needle isn't inserted deep enough, insulin may not be absorbed properly, affecting blood sugar control.
Tissue Damage: Repeated incorrect angles can lead to lipohypertrophy or scarring, which can interfere with insulin absorption.
Choose the Right Needle Length: Shorter needles (4mm or 6mm) are typically recommended for those with less subcutaneous fat.
Use the Correct Angle: Insert the needle at a 90-degree angle for most people, and at a 45-degree angle for thinner individuals.
Pinch the Skin: Pinching helps ensure the insulin is injected into the subcutaneous layer, especially for people with more fat.
Inject Quickly: A quick, steady insertion minimizes pain and reduces the risk of tissue damage.
Avoid Scarred Areas: Inject into clean, flat areas to prevent discomfort and ensure effective insulin absorption.
Following these tips will ensure smoother, more effective insulin injections, improving your diabetes management.
Rotating your injection sites is crucial to ensure consistent insulin absorption and prevent complications like lipohypertrophy (fat build-up at the injection site). Repeatedly using the same spot can lead to the development of lumps or hardened tissue, which can make insulin less effective. By rotating your sites, you allow the tissue to heal and ensure that insulin is properly absorbed each time.
Decreased Effectiveness of Insulin: Insulin may not be absorbed properly if injected into scarred or fatty tissue, leading to fluctuations in blood sugar levels.
Potential for Scarring: Repeated injections in the same area can cause permanent damage, making it difficult to inject or affect the absorption of insulin.
Plan Your Rotation: Common areas for insulin injections include the abdomen, thighs, and upper arms. Ensure you rotate through these areas to avoid constant use of the same site.
Avoid the Same Spot Twice in a Row: Try to inject at least 1 inch away from the previous site to prevent irritation or build-up.
Mark Your Sites: Keep track of where you've injected recently to help you rotate properly. Consider using a notebook or a tracking app.
Use a New Area of the Skin: Within each injection site (abdomen, thigh, etc.), change the exact spot by moving slightly over to prevent using the same area repeatedly.
By following these practices, you can ensure better insulin absorption, avoid complications, and maintain smoother injections for effective diabetes management.
Proper storage of your insulin injection pen is crucial to maintain the potency of the insulin.
Unused Pens: Keep unopened pens in the refrigerator at a temperature between 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C). Never freeze the insulin, as freezing can damage the medication.
Active Pens: Once the pen is in use, it should be stored at room temperature (up to 77°F or 25°C) to avoid degradation. Most pens are stable at room temperature for about 28 days, but always check the specific instructions for your insulin type.
Storing insulin pens incorrectly can cause the insulin to degrade, making it less effective or even completely ineffective. If insulin is exposed to extreme temperatures (either too hot or too cold), it may lose its ability to control blood sugar levels, leading to poor diabetes management. Additionally, insulin stored improperly can cause irritation at the injection site or lead to other adverse reactions.
Store Unused Pens in the Refrigerator: Always store unopened pens in the fridge to maintain insulin’s effectiveness. Just be sure to remove the pen from the fridge 30 minutes before use to avoid discomfort from cold insulin.
Store Active Pens at Room Temperature: After opening, keep your insulin pen at room temperature. Avoid storing it near heat sources, such as radiators or in direct sunlight.
Check Expiration Dates: Regularly check the expiration date on the pen and insulin cartridge. Expired insulin may not work properly, so discard any expired pens or cartridges.
Avoid Freezing: Never freeze insulin pens, as freezing can damage the insulin. If the pen has been frozen, discard it and use a new one.
Use a Protective Case: Consider using a case or carrying pouch to protect the pen from temperature extremes while traveling.
By following these storage guidelines, you can ensure that your insulin injection pen remains effective and safe for use, helping you maintain better control over your diabetes management.
Answer: If you miss a dose, check your blood sugar and follow your healthcare provider's instructions. They may recommend taking the missed dose or adjusting your schedule. Always consult your doctor for guidance.
Answer: If the pen appears undamaged and the insulin is still within its expiration date, it should be fine to use. However, if the pen is cracked or broken, discard it and use a new one.
Answer: Replace the needle every time you inject insulin. Reusing needles can cause discomfort, infection, and affect injection quality.
Answer: Yes, but make sure it’s kept at room temperature and protected from sunlight. Using a case can help prevent damage while you're on the go.
In conclusion, using an insulin injection pen effectively requires attention to detail and adherence to proper practices. Whether it’s managing missed doses, handling the pen with care, or ensuring the needle is replaced regularly, taking the time to follow the right steps will help maintain proper insulin delivery and effective diabetes management. Storing your pen correctly and consulting with a healthcare provider when necessary will further ensure that you get the most out of your insulin therapy. By avoiding common mistakes and using your insulin pen with confidence, you can better control your blood sugar and improve your overall health.